Are you curious about Information Technology Infrastructure Library, commonly known as ITIL? Have you ever wondered how it can shake up your organization’s way of providing IT services? In a tech-heavy workplace, we’ll demystify ITIL—explaining the brief history, what it is, why it is necessity, how it works, benefits of ITIL within the organization, and a guide where and how to start your ITIL journey.
History of ITIL
The journey of ITIL’s evolution has been a captivating one, mirroring the rapidly changing landscape of information technology and the dynamic needs of businesses.
In the 1980s, as businesses increasingly leaned on IT services, a group of UK-based IT professionals recognized the necessity for a standardized approach. This led to the inception of ITIL (Version 1) in 1990, a collection of practices for IT service management (ITSM) with a specific focus on vendor practices.
In the early 2000s, acknowledging the escalating reliance on technology, ITIL (Version 2) took a more encompassing approach to service delivery and support, offering a set of best practices for IT processes and functions. This era saw ITIL gaining global recognition, establishing itself as a standard for managing computer services.
With the recognition of IT as a strategic advantage, ITIL (Version 3) updated its framework to become more holistic, emphasizing strategy, design, transition, operation, and continual service improvement. And as recent as 2019, ITIL 4 incorporated modern service management concepts like agile and DevOps, introducing the idea of co-creating value with customers.
Throughout its evolution, ITIL has played a pivotal role in shaping how organizations manage and deliver IT services. Starting as a detailed framework, it progressed into streamlined versions, and now, with ITIL 4, it continues to adapt, remaining relevant, adaptable, and aligned with contemporary IT practices. As the latest version, ITIL4 underscores its ongoing commitment to providing a roadmap for IT services that seamlessly integrates with the ever-changing IT landscape.
What is ITIL?
In a nutshell, ITIL comprises a set of best practices and guidelines geared towards effectively managing and delivering IT services while prioritizing alignment with the organization’s needs. The flexibility and adaptability of the ITIL framework are notable; it doesn’t rigidly mandate adherence to every aspect but rather encourages a service-oriented approach, seamlessly integrating IT into the broader business strategy.
Encompassing various processes and practices such as service strategy, service design, service transition, service operation, and continual service improvement, ITIL is structured to assist organizations in meeting their primary goal of improved efficiency and customer satisfaction.
The Importance in Today’s Modern IT Landscape
Today, ITIL is designed to address various challenges and problems faced by organizations in managing IT services. Some common problems that ITIL aims to solve include:
Lack of Standardization Leading to Inefficient Service Delivery: Organizations often face challenges due to the absence of standardized practices. Without any clear processes for strategy, design, transition, operation, and continual improvement, most company initiatives are shoot anywhere – acting quickly without careful planning or consideration.
Poor Communication and Collaboration: Poor communication and collaboration across different departments leads to repetitive messaging, duplicated efforts, as well as ineffective problem solving.
Inadequate Change Management. Change management does not just refer to users accepting the necessary changes or avoiding any issues or disruptions. More importantly, it’s introducing strategic technology initiatives to make the organization more competitive.
Limited Focus on Customer Needs. Crucially, the customer can encompass both the organization and the end-user. When there is insufficient attention given to understanding the customer—neglecting their challenges, concerns, and goals—achieving an exceptional customer experience and unlocking their full potential becomes unattainable through any technological initiatives.
Lack of Continual Improvement Mindset. Having the right mindset is crucial, and it’s often prevalent among organizational leaders. Without embracing this mindset, and with the increased reliance on technology, organizations will stagnate. Remaining stagnant results in a diminished strategic advantage, as resources are underutilized and the customer experience remains unchanged. This leaves organizations vulnerable to challenges from competitors.
How ITIL Operates
The Guiding Principles
It begins with the guiding principles, a set of fundamental concepts that guide organizations in their decision-making and actions when adopting ITIL practices. These principles are designed to be simple and universally applicable.
Focus on Value. Prioritize actions and decisions based on the value they bring to the business and its customers. By assessing the value the initiative brings in relation to the associated costs, organizations are able to optimize for maximum impact.
Start Where You Are. Start your journey of improvement from where you are now; there’s no need to begin anew. Build upon your existing foundation, as the positive outcomes from past initiatives should not be squandered. Undertake new initiatives only if the benefits justify the effort.
Progress Iteratively with Feedback. Make continuous improvement through incremental steps, gaining insights from each round and adjusting as necessary. By maintaining a manageable project size, costs decrease while you accumulate knowledge, both positive and negative, from each undertaking.
Collaborate and Promote Visibility. Encourages collaboration and transparent communication, ensuring everyone is aligned and striving for shared objectives. This helps steer clear of typical project issues like blaming or personal biases.
Think and Work Holistically. Thinking about the whole service journey and how all the pieces connect instead of just looking at individual parts.
Keep It Simple and Practical. Straightforward approaches are usually optimal, cutting costs and minimizing the chances of failures.
Optimize and Automate: Look for opportunities to streamline processes and incorporate automation to enhance efficiency and reduce errors.
Be Transparent: Be open and honest in communication, sharing information to build trust and ensure everyone has a clear understanding of what’s happening.
By following these guiding principles, organizations can better align their IT services with business goals, improve efficiency, and provide enhanced value to customers.
If you’re curious on iterative development (Agile), read our article on Scrum – Scrum Simplified: Completing Projects Ahead of Time
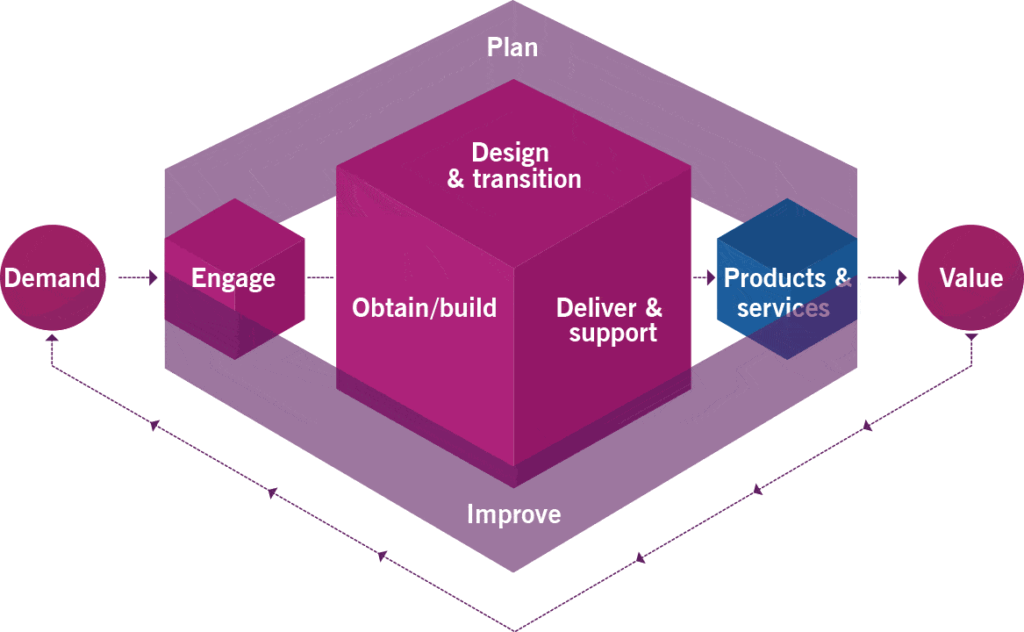
The Service Value Chain (SVC)
Beyond the guiding principles, the Service Value Chain is a tangible plan for developing, providing, and improving services. It shows the different steps that an organization can follow to make things valuable for their customers.
While we won’t explore the specific elements of the Service Value Chain in detail, it is crafted to align with the guiding principles and practices of ITIL 4. This enables organizations to visualize and oversee the progression of activities in the end-to-end service delivery process.
The ITIL Management Practices
Separately, the ITIL Management Practices refers to specific sets of organizational resources and capabilities designed for performing work, managing activities, and achieving specific objectives. These practices are essential components of the ITIL framework, which provides guidance on IT service management (ITSM). Here are some of the practices:
General Management Practices
Continual Improvement. Focuses on regularly improving services and processes.
Information Security Management. Ensures that information security aligns with the organization’s needs.
Service Management Practices
Incident Management. Handles the lifecycle of incidents, from identification to resolution.
Problem Management. Focuses on identifying and addressing the root causes of incidents.
Change Enablement. Manages changes in a coordinated way to improve services.
Service Request Management. Addresses standard service requests, helping users get what they need.
Service Desk. Provides a single point of contact for users to get help and information.
Technical Management Practices
Deployment Management. Ensures the proper deployment of services and releases.
Infrastructure and Platform Management. Manages the technology infrastructure and platforms.
Software Development and Management. Guides the development and maintenance of custom software.
Each practice includes specific activities, roles, and workflows to help organizations effectively manage their IT services. These practices are designed to be adaptable and can be tailored to fit the unique needs and circumstances of different organizations.
Unlocking Organizational Success with ITIL
After a quick look at ITIL, it’s evident that it can benefit crucial aspects of organizations by cutting costs, enhancing service quality, aligning with business goals, while being adaptable. The most significant advantages of incorporating ITIL in these areas include:
Improving Customer Satisfaction. Aligning IT services with business needs improves customer satisfaction. Standardizing processes ensures consistent, high-quality service delivery.
Efficient Change Management. Structured change management ensures planned and tested implementations, minimizing disruptions.
Cost Reduction. Identifying and eliminating unnecessary processes leads to operational cost savings.
Alignment with Business Objectives. ITIL ensures IT services support the overall strategic goals of the organization.
Continuous Improvement. ITIL promotes a culture of ongoing assessment and optimization of processes for adaptability.
Where to Start ITIL?
Now that we know what ITIL brings to the table, and the benefits it provides. Where to start? Here’s a straightforward guide which involves a structured approach to ensure effective integration within your organization:
-
Consider Your Motivation. To kickstart your journey with ITIL, take a close look at why you want to do it. It’s common for many to first focus on the technology without grasping the true goal—it’s about solving an existing problem. Business leaders should have clear and solid reasons for embracing ITIL and should understand how it will bring benefits to the business.
-
Develop Knowledge and Expertise. Implementing ITIL calls for expertise—it’s not something you can just pick up from a manual. Business leaders should depend on someone (or a few individuals) with proper ITIL certification and proven expertise to lead the way. This might involve some new training or bringing in consultants to ensure the necessary know-how for ITIL conformance.
-
Start Small and Grow. Begin by trying out one or a few ITIL practices on a small scale to see how they affect your organization. Understand your people, processes, and technology as you implement them. Then, reassess to pinpoint what’s crucial for a successful rollout. Document the current process, its strengths and weaknesses, and assess how it affects business performance after adoption. Why reassess? It helps fine-tune your approach based on what you’ve learned initially. Gradually expand small projects that demonstrate value, adding more practices as necessary. This ensures a smoother and more effective integration of ITIL practices.
-
Focus on Achieving Outcomes. Outcomes refer to the actual results achieved through ITIL implementation, such as improved customer satisfaction or reduced service costs. ITIL itself is not the ultimate goal. The goal lies in defining and achieving specific business objectives. By measuring outcomes through metrics, organizations ensure that ITIL compliance aligns with and contributes to broader business success.
Briefly introducing ITIL, we explored its multifaceted benefits, ranging from cost reduction to enhanced service quality and adaptability. The implementation of ITIL is not a daunting task; instead, it involves a structured and thoughtful approach. By starting with small trials, understanding the nuances of people, processes, and technology, and reassessing based on initial learnings, organizations can smoothly integrate ITIL practices.
If you’re curious and interested in exploring more about how ITIL works or contemplating its integration into your organization, let’s talk. Send an email to hello@corqspace.com. Rest assured, it’s commitment free. We take pleasure in assisting companies with their digital transformation. If you like our content, follow us on Linkedin. We share the latest news related to technology in the workplace.




